In-Short
- MIT researchers develop a new robot training method called Heterogeneous Pretrained Transformers (HPT).
- HPT improves training efficiency and adaptability by using diverse data from multiple sources.
- The system outperforms traditional methods, showing promise for a universal robot brain.
Summary of MIT’s Robot Training Breakthrough
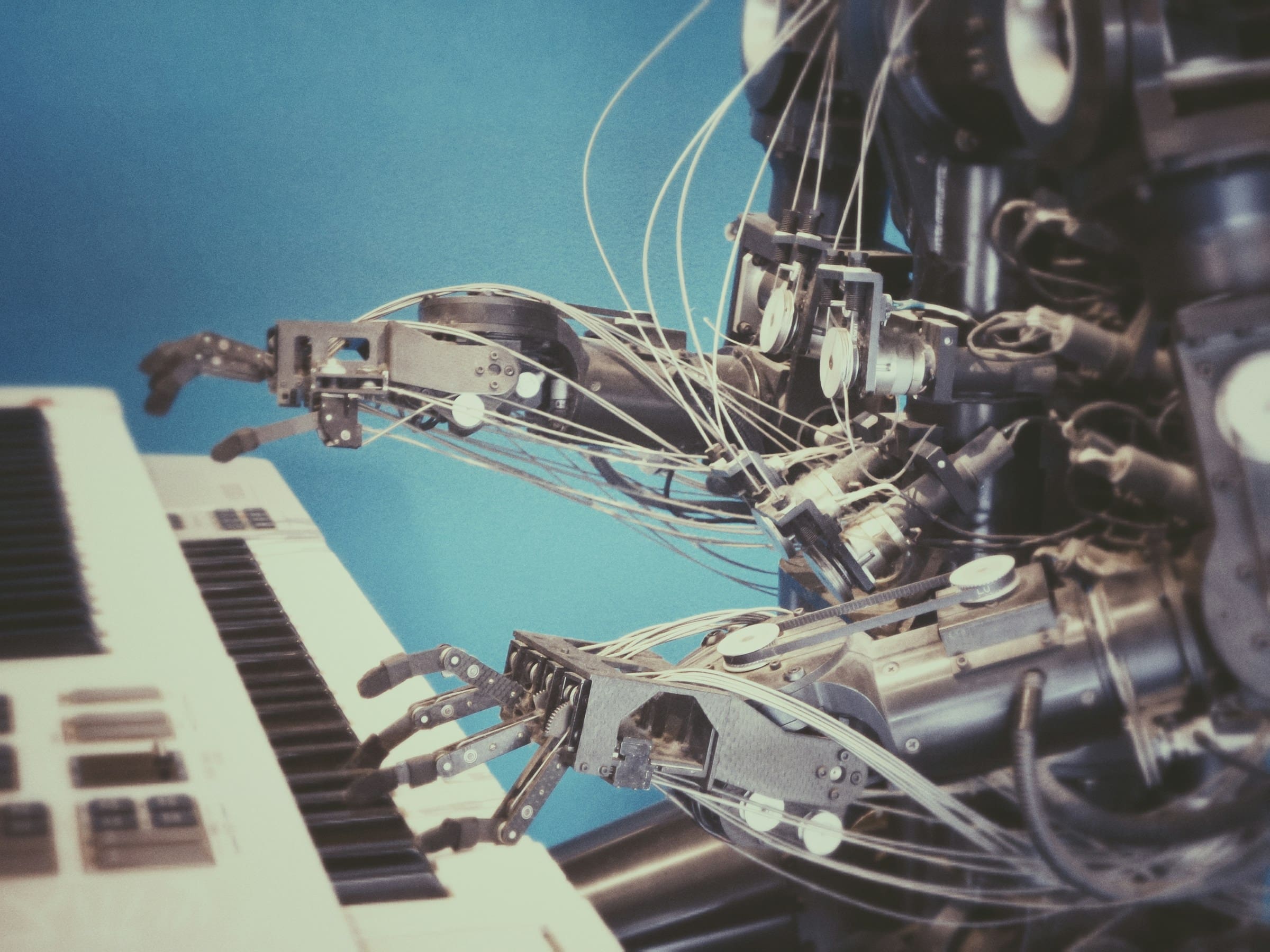
MIT researchers have introduced a groundbreaking approach to robot training that promises to reduce time and costs while enhancing adaptability. The method, known as Heterogeneous Pretrained Transformers (HPT), leverages a vast array of diverse data, integrating it into a unified system. This innovation allows robots to understand and process information more effectively, akin to a shared language for generative AI models.
Lirui Wang, the lead researcher and a graduate student at MIT, emphasizes the significance of their work in addressing the challenges posed by the diversity of domains, modalities, and robot hardware in robotics. The HPT architecture they developed is capable of unifying different data types, such as camera images, language instructions, and depth maps, using a transformer model to process visual and proprioceptive inputs.
In practical applications, HPT has demonstrated impressive results, surpassing traditional training methods by over 20% in both simulated and real-world environments. This is particularly notable when robots face tasks that differ greatly from their training data. The researchers’ dataset for pretraining includes over 200,000 robot trajectories from 52 datasets, allowing robots to learn from a broad range of experiences.
One of the key features of HPT is its emphasis on proprioception, which is the robot’s awareness of its own position and movement. This focus enables robots to perform more complex and dexterous motions. The team’s future goals include improving HPT’s ability to process unlabelled data and developing a universal robot brain that could be applied to any robot without the need for additional training.
While still in the early stages, the researchers are optimistic that scaling HPT could lead to significant advancements in robotic policies, drawing parallels to the progress made with large language models.
Further Reading and Image Credit
For a more in-depth understanding of this innovative robot training method and its potential impact on the future of robotics, readers are encouraged to view the original article. Click here to read the full article.
Image credit: Possessed Photography